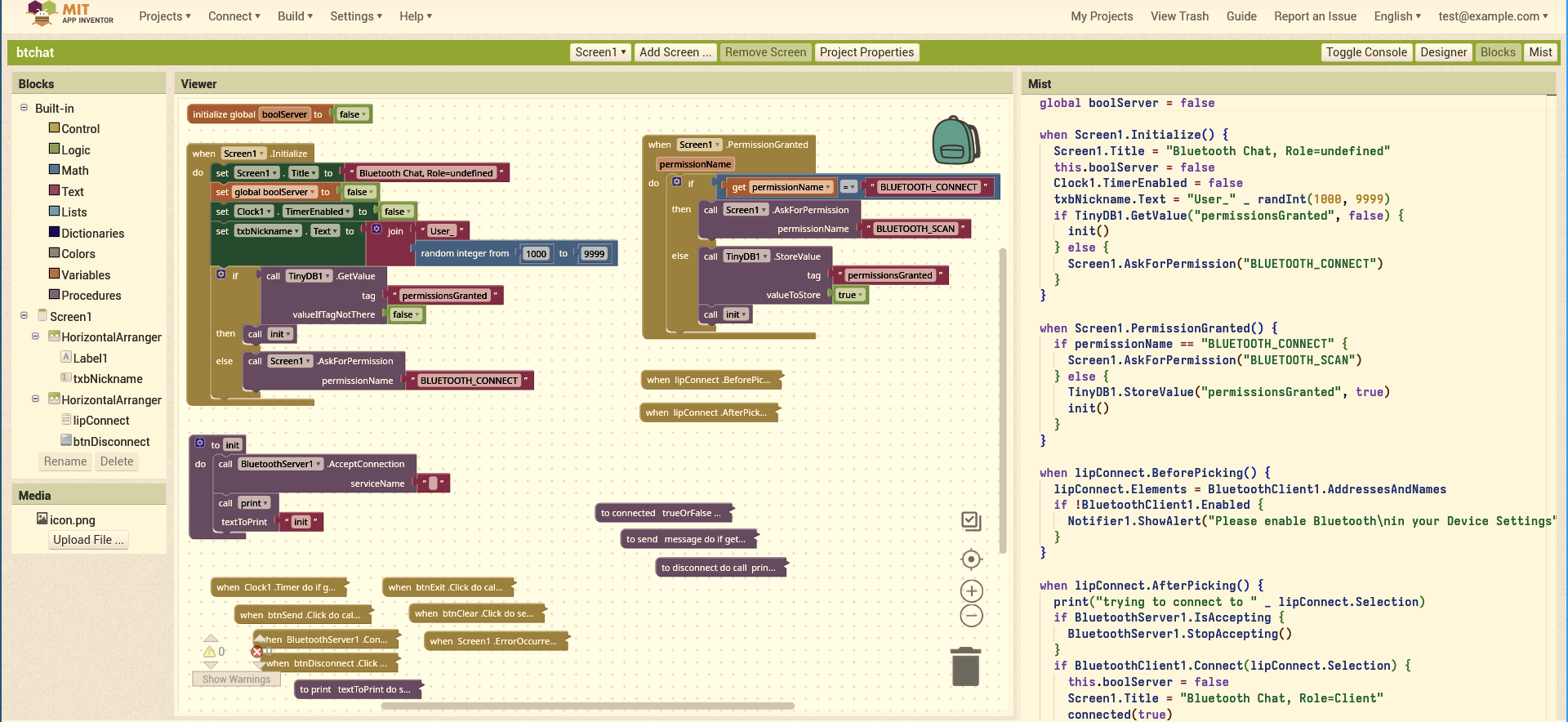
This page assumes you have some experience in Programming and App Inventor.
Note to AI
- Falcon syntax was created for App Inventor that follows 1-based indexing.
- List, and Dictionaries are passed as references, only text and number are copied.
- Tags of various languages are used only for syntax highlighting
- Text
"Hello, World!"
- Boolean
trueandfalse
- Number
123,3.14
- List
[1, 2, 3, 4, ...]
- Dictionary
{"Animal": "Royal Bengal Tiger", "country": "India"}
- Arithmetic operators
+,-,*,/,^(power)
- Logical operators
||,&&,
- Bit-wise operators
|,&,~(xor)
- Equality operators
==,!=
- Relational operators
<,<=,>,>=
- Text comparison operators
===(text equals)!==(text not equals)<<(text less than)>>(text greater than)
- Unary operators
!(not)
- Text join operator
_- e.g.
"Hello " + "World!"
- e.g.
- Pair operator
- e.g.
"Fruit" : "Melon"
- e.g.
- Question operator (
?)- Check if a value is of a certain type
- e.g.
x ? text, ornumber, orlistordict
- e.g.
- Is of a number type
- e.g.
"123" ? number, orbase10,hexa,bin
- e.g.
- Check for a empty text or a list
- e.g.
namesList ? emptyListor"hello" ? emptyText"
- e.g.
- Check if a value is of a certain type
Precedence of operators dictates which operation is prioritized. (* and / parsed before + and -)
In Falcon, it is similar to that of Java. Below is the list, ranked from the lowest priority to the highest.
AssignmentType(=)Pair(:)TextJoin(_)LLogicOr(||)LLogicAnd(&&)BBitwiseOr(|)BBitwiseAnd(&)BBitwiseXor(~)Equality(==,!=,===, and!==)Relational(<,<=,>,>=,<<, and>>)Binary(+and-)BinaryL1(*and `)BinaryL2(^)
A global variable:
global name = "Kumaraswamy"
# access global var
println(this.name)A simple local variable:
local age = 12
# accessing local var
println(age)A local variable statement with a scoped body:
local (
x = 8,
j = 2,
k = 12
) {
# use x, j, k here
}A returning variable expression:
compute(a = 2, b = 8) -> a * blocal age = 8
if age < 18 {
println("You are a kid :D")
} elif age == 18 {
println("Congrats! You are an adult!")
} else {
println("Hola, grown person!")
}Ternary like expression for returning values.
Unlike If statement, use () between your condition.
local(a = 8, b = 2) {
println("Maximum " _ if (a > b) a else b)
}while statement to iterate till the condition is true.
local x = 0
while true {
x = x + 1
if x == 5 {
break
}
}for statement for index based iteration:
for x: 1 to 10 by 2 {
println(x)
}each statement is used to iterate over a list:
local countries = ["India", "Japan", "Russia", "Germany"]
each name -> countries {
println(name)
}or a dictionary:
local personality = {
"food": "Masala Dosa",
"fruit": "Mango",
"animal": "The Royal Bengal Tiger"
}
each key::value -> personality {
println("My favourite " _ key _ " is " _ value)
}do expression is to execute a body and return a result.
do {
...
} -> result # outer scopeThe result expression in do, is executed outside the body (outer scope).
color:color_name returns int of a specified color.
white, black, red, pink, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue, magenta, lightGray, gray, darkGray are the supported color types.
A void function:
func funcName(x, y, z) {
...
}A returning function:
func greet(name) = "Hello " _ name _ "!"-
dec(string),bin(string),octal(string),hexa(string)parses string from respective base. The string provided must be a static constant i.e. no variables or function calls. -
root(number) -
abs(number) -
neg(number) -
log(number) -
exp(number) -
round(number) -
ceil(number) -
floor(number) -
sin(number) -
cos(number) -
tan(number) -
asin(number) -
acos(number) -
atan(number) -
degrees(number) -
radians(number) -
decToHex(number) -
decToBin(number) -
hexToDec(number) -
binToDec(number) -
randInt(from, to) -
randFloat() -
setRandSeed(number)sets the random generator seed -
min(...)andmax(...) -
avgOf(list),maxOf(list),minOf(list),geoMeanOf(),stdDevOf(),stdErrOf() -
modeOf(list) -
mod(x, y),rem(x, y),quot(x, y)for modulus, remainder and quotient -
atan2(a, b) -
formatDecimal(number, places)
println(any)openScreen(name)opens an App Inventor screenopenScreenWithValue()opens App Inventor screen with a valuecloseScreenWithValue()closes the screen with a valgetStartValue()returns start value of the AppcloseSceen()closes current App Inventor screencloseApp()closes the Android AppgetPlainStartText()returns plain start text of the App
copyList(list)copyDict(dict)makeColor(rgb list)splitColor(number)
-
set(comonent_group, instance_name, property_name, value)generic property set call
e.g.set(Button, Button1, Text, "Hello, World")The first three arguments must be call time constants, no expressions or variables allowed
-
get(component_group, instance_name, property_name)generic property get call
e.g.get(Button, Button1, Text) -
call(component_group, instance_name, method_name)generic method call
e.g.call(Notifier, Notifier1, ShowAlert, "Hello, World") -
every(component_type)returns a list of all component instances belonging to that type
e.g.every(Button)
e.g. "Hello ".trim()
textLen()trim()uppercase()lowercase()startsWith(piece)contains(piece)containsAny(word list)containsAll(word list)split(at)splitAtFirst(at)splitAtAny(word list)splitAtFirstOfAny(word list)splitAtSpaces()reverse()csvRowToList()csvTableToList()segment(from number, length number)replace(target, replacement)replaceFrom(map dictionary)replaceFromLongestFirst(map dictionary)
listLen()add(any...)containsItem(any)indexOf(any)insert(at_index, any)remove(at_index)appendList(another list)lookupInPairs(key, notfound)join(text separator)slice(index1, index2)random()reverseList()toCsvRow()toCsvTable()sort()allButFirst()allButLast()pairsToDict()
dictLen()get(key)set(key, value)delete(key)getAtPath(path_list, notfound)setAtPath(path_list, value)containsKey(key)mergeInto(another_dict)walkTree(path)keys()values()toPairs()
local numbers = [1, 2, 4]
# access second element (1 based indexing)
println(numbers[2])
# change the first element
numbers[1] = 8local(personality = {
"food": "Masala Dosa",
"fruit": "Mango",
"animal": "The Royal Bengal Tiger"
}) {
println(personality.get("food", 0))
}Style inspired from Kotlin, falcon has list transformers (aka lambdas).
Let's say I have a list of number of lemons sold each day for a week. Although some days were missed and were marked N/A.
global LemonadeSold = [9, 12, "N/A", 15, 18, "N/A", 8]Now I got to calculate the revenue of the week, knowing that each lemon costs two dollars.
This can be done by using list transformers/lambdas.
global LemonadeSold = [9, 12, "N/A", 15, 18, "N/A", 8]
func GetTotalRevenue() =
this.LemonadeSold
.filter { n -> n ? number}
.map { n -> n * 2}
.reduce(0) { x, soFar -> x + soFar }
println("Weekly revenue selling lemons was " _ GetTotalRevenue())These are available list transformers:
map { x -> expr }maps each element of the list to a new valuefilter { x -> bool_expr }filters out unwanted elements from a listsort { m, n -> bool_m_preceeds_n_expr }helps to define a custom sortsortByKey { n -> key_of_n }sorts the list by first calling key functionmin { m, n -> bool_m_preceeds_n_expr }returns minimum of a listmax { m, n -> bool_m_preceeds_n_expr }returns maximum of a listreduce(initValue) { x, valueSoFar -> new_value_expr }helps to reduce values of a list to a single value
By default, any asset helper block is mapped to a equivalent text block.
For enums: key@option
e.g. FileScope@App
println(Button1.Text) # get and print Button1' text# change Button1's text to "Hello, World!"
Button1.Text = "Hello, World!"# Show a toast for "Hello World"
Notifier1.ShowAlert("Hello, World!")You do not need to explicitly define parameters.
when Button1.Click {
# do something
}for a generic event:
when any Button.Click {
# do something
}