Manage llama.cpp servers like Ollama—but faster. Full control over llama-server with macOS launchctl integration.
CLI tool to manage local llama.cpp servers on macOS. Provides an Ollama-like experience for managing GGUF models and llama-server instances, with significantly faster response times than Ollama.
Status: Beta - Stable for personal use, actively maintained
- 🚀 Easy server management - Start, stop, and monitor llama.cpp servers
- 🔀 Unified router - Single OpenAI-compatible endpoint for all models with automatic routing and request logging
- 🌐 Admin Interface - REST API + modern web UI for remote management and automation
- 🤖 Model downloads - Pull GGUF models from Hugging Face
- 📦 Models Management TUI - Browse, search, and delete models without leaving the TUI. Search HuggingFace, download with progress tracking, manage local models
- ⚙️ Smart defaults - Auto-configure threads, context size, and GPU layers based on model size
- 🔌 Auto port assignment - Automatically find available ports (9000-9999)
- 📊 Real-time monitoring TUI - Multi-server dashboard with drill-down details, live GPU/CPU/memory metrics, token generation speeds, and animated loading states
- 🪵 Smart logging - Compact one-line request format with optional full JSON details
- ⚡️ Optimized metrics - Batch collection and caching prevent CPU spikes (10x fewer processes)
TL;DR: Much faster response times than Ollama by using llama.cpp's native server directly.
Ollama is great, but it adds a wrapper layer that introduces latency. llamacpp-cli gives you:
- ⚡️ Faster inference - Direct llama-server means lower overhead and quicker responses
- 🎛️ Full control - Access all llama-server flags and configuration options
- 🔧 Transparency - Standard launchctl services, visible in Activity Monitor
- 📦 Any GGUF model - Not limited to Ollama's model library
- 🪶 Lightweight - No daemon overhead, just native macOS services
| Feature | llamacpp-cli | Ollama |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | ⚡️ Faster (native) | Slower (wrapper layer) |
| Model Format | Any GGUF from HF | Ollama's library |
| Server Binary | llama.cpp native | Custom wrapper |
| Configuration | Full llama-server flags | Limited options |
| Service Management | macOS launchctl | Custom daemon |
| Resource Usage | Lower overhead | Higher overhead |
| Transparency | Standard Unix tools | Black box |
If you need raw speed and full control, llamacpp-cli is the better choice.
llamacpp-cli offers three ways to manage your servers:
| Interface | Best For | Access | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLI | Local development, automation scripts | Terminal | Full control, shell scripting, fastest for local tasks |
| Router | Single endpoint for all models | Any OpenAI client | Model-based routing, streaming, zero config |
| Admin | Remote management, team access | REST API + Web browser | Full CRUD, web UI, API automation, remote control |
When to use each:
- CLI - Local development, scripting, full terminal control
- Router - Using with LLM frameworks (LangChain, LlamaIndex), multi-model apps
- Admin - Remote access, team collaboration, browser-based management, CI/CD pipelines
npm install -g @appkit/llamacpp-cli- macOS (uses launchctl for service management)
- llama.cpp installed via Homebrew:
brew install llama.cpp
# Search for models on Hugging Face
llamacpp search "llama 3b"
# Download a model
llamacpp pull bartowski/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-GGUF/llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf
# List local models
llamacpp ls
# Create and start a server (auto-assigns port, uses smart defaults)
llamacpp server create llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf
# Open interactive TUI dashboard (multi-server monitoring)
llamacpp
# Press 'M' to access Models Management TUI
# List all servers (static table)
llamacpp ps
# View log sizes for all servers
llamacpp logs
# Chat with your model interactively
llamacpp server run llama-3.2-3b
# Or send a single message (non-interactive)
llamacpp server run llama-3.2-3b -m "What is the capital of France?"
# Stop a server
llamacpp server stop llama-3.2-3b
# Start a stopped server
llamacpp server start llama-3.2-3b
# View logs
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b -f
# Start admin interface (REST API + Web UI)
llamacpp admin start
# Access web UI at http://localhost:9200Once a server is running, it exposes an OpenAI-compatible API:
# Chat completion
curl http://localhost:9000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the capital of France?"}
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 100
}'
# Text completion
curl http://localhost:9000/v1/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"prompt": "Once upon a time",
"max_tokens": 50
}'
# Get embeddings
curl http://localhost:9000/v1/embeddings \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": "Hello world"
}'
# Health check
curl http://localhost:9000/healthThe server is fully compatible with OpenAI's API format, so you can use it with any OpenAI-compatible client library.
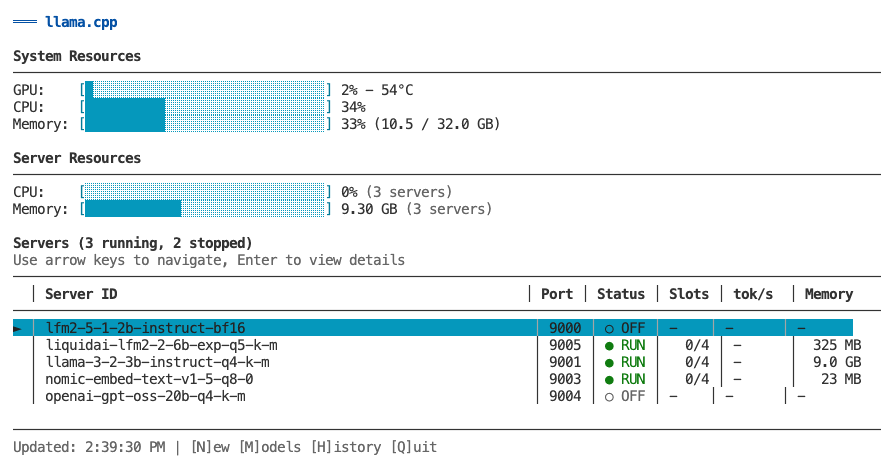
The primary way to manage and monitor your llama.cpp servers is through the interactive TUI dashboard. Launch it by running llamacpp with no arguments.
llamacppThe TUI provides a comprehensive interface for:
- Monitoring - Real-time metrics for all servers (GPU, CPU, memory, token generation)
- Server Management - Create, start, stop, remove, and configure servers
- Model Management - Browse, search, download, and delete models
- Historical Metrics - View time-series charts of past performance
The main view shows all your servers at a glance:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ System Resources │
│ GPU: [████░░░] 65% CPU: [███░░░] 38% Memory: 58% │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Servers (3 running, 0 stopped) │
│ │ Server ID │ Port │ Status │ Slots │ tok/s │
│───┼────────────────┼──────┼────────┼───────┼──────────┤
│ ► │ llama-3-2-3b │ 9000 │ ● RUN │ 2/4 │ 245 │ (highlighted)
│ │ qwen2-7b │ 9001 │ ● RUN │ 1/4 │ 198 │
│ │ llama-3-1-8b │ 9002 │ ○ IDLE │ 0/4 │ - │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↑/↓ Navigate | Enter for details | [N]ew [M]odels [H]istory [Q]uit
Features:
- System resource overview (GPU, CPU, memory)
- List of all servers (running and stopped)
- Real-time status updates every 2 seconds
- Color-coded status indicators
- Navigate with arrow keys or vim keys (k/j)
Press Enter on any server to see detailed information:
Running servers show:
- Server information (status, uptime, model name, endpoint)
- Request metrics (active/idle slots, prompt speed, generation speed)
- Active slots detail (per-slot token generation rates)
- System resources (GPU/CPU/ANE utilization, memory usage)
Stopped servers show:
- Server configuration (threads, context, GPU layers)
- Last activity timestamps
- Quick action commands (start, config, logs)
Press M from the main view to access Models Management.
Features:
- Browse all installed models with size and modified date
- View which servers are using each model
- Delete models with cascade option (removes associated servers)
- Search HuggingFace for new models
- Download models with real-time progress tracking
Models View:
- View all GGUF files in scrollable table
- Color-coded server usage (green = safe to delete, yellow = in use)
- Delete selected model with
EnterorDkey - Confirmation dialog with cascade warning
Search View (press S from Models view):
- Search HuggingFace models by text input
- Browse results with downloads, likes, and file counts
- Expand model to show available GGUF files
- Download with real-time progress, speed, and ETA
- Cancel download with
ESC(cleans up partial files)
Create Server (press N from main view):
- Select model from list (shows existing servers per model)
- Edit configuration (threads, context size, GPU layers, port)
- Review smart defaults based on model size
- Create and automatically start server
- Return to main view with new server visible
Start/Stop Server (press S from detail view):
- Toggle server state with progress modal
- Stays in detail view after operation
- Shows updated status immediately
Remove Server (press R from detail view):
- Confirmation dialog with option to delete model file
- Warns if other servers use the same model
- Cascade deletion removes all associated data
- Returns to main view after deletion
Configure Server (press C from detail view):
- Edit all server parameters inline
- Modal dialogs for different field types
- Model migration support (handles server ID changes)
- Automatic restart prompts for running servers
- Port conflict detection and validation
Press H from any view to see historical time-series charts.
Single-Server Historical View:
- Token generation speed over time
- GPU usage (%) with avg/max/min stats
- CPU usage (%) with avg/max/min
- Memory usage (%) with avg/max/min
- Auto-refresh every 3 seconds
Multi-Server Historical View:
- Aggregated metrics across all servers
- Total token generation speed (sum)
- System GPU usage (average)
- Total CPU usage (sum of per-process)
- Total memory usage (sum in GB)
View Modes (toggle with H key):
-
Recent View (default):
- Shows last 40-80 samples (~1-3 minutes)
- Raw data with no downsampling - perfect accuracy
- Best for: "What's happening right now?"
-
Hour View:
- Shows all ~1,800 samples from last hour
- Absolute time-aligned downsampling (30:1 ratio)
- Bucket max for GPU/CPU/token speed (preserves peaks)
- Bucket mean for memory (shows average)
- Chart stays perfectly stable as data streams in
- Best for: "What happened over the last hour?"
Data Collection:
- Automatic during monitoring (piggyback on polling loop)
- Stored in
~/.llamacpp/history/<server-id>.jsonper server - Retention: Last 24 hours (circular buffer, auto-prune)
- File size: ~21 MB per server for 24h @ 2s interval
List View (Multi-Server):
↑/↓ork/j- Navigate server listEnter- View details for selected serverN- Create new serverM- Switch to Models ManagementH- View historical metrics (all servers)ESC- Exit TUIQ- Quit immediately
Detail View (Single-Server):
S- Start/Stop server (toggles based on status)C- Open configuration screenR- Remove server (with confirmation)H- View historical metrics (this server)ESC- Back to list viewQ- Quit immediately
Models View:
↑/↓ork/j- Navigate model listEnterorD- Delete selected modelS- Open search viewR- Refresh model listESC- Back to main viewQ- Quit immediately
Search View:
/orI- Focus search inputEnter(in input) - Execute search↑/↓ork/j- Navigate results or filesEnter(on result) - Show GGUF files for modelEnter(on file) - Download/install modelR- Refresh results (re-execute search)ESC- Back to models view (or results list if viewing files)Q- Quit immediately
Historical View:
H- Toggle between Recent/Hour viewESC- Return to live monitoringQ- Quit immediately
Configuration Screen:
↑/↓ork/j- Navigate fieldsEnter- Open modal for selected fieldS- Save changes (prompts for restart if running)ESC- Cancel (prompts if unsaved changes)Q- Quit immediately
For GPU and CPU utilization metrics, install macmon:
brew install vladkens/tap/macmonWithout macmon, the TUI still shows:
- ✅ Server status and uptime
- ✅ Active slots and token generation speeds
- ✅ Memory usage (via built-in vm_stat)
- ❌ GPU/CPU/ANE utilization (requires macmon)
The llamacpp server monitor command is deprecated. Use llamacpp instead to launch the TUI dashboard.
The router provides a single OpenAI-compatible endpoint that automatically routes requests to the correct backend server based on the model name. This is perfect for LLM clients that don't support multiple endpoints.
# Start the router (default port: 9100)
llamacpp router start
# Configure your LLM client to use http://localhost:9100
# The router automatically routes requests to the correct server based on model namellamacpp router start # Start the router service
llamacpp router stop # Stop the router service
llamacpp router status # Show router status and available models
llamacpp router restart # Restart the router
llamacpp router config # Update router settings (--port, --host, --timeout, --health-interval, --verbose)
llamacpp router logs # View router logs (with --follow, --verbose, --clear options)The router acts as a single endpoint for all your models:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
base_url="http://localhost:9100/v1",
api_key="not-needed" # API key not required for local servers
)
# Router automatically routes to the correct server based on model name
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
)POST /v1/chat/completions- Chat completions (routes to correct backend)POST /v1/embeddings- Text embeddings (routes to correct backend)GET /v1/models- List all available models from running serversGET /health- Router health check
The router can be configured with:
# Change port
llamacpp router config --port 9200 --restart
# Update request timeout (ms)
llamacpp router config --timeout 60000 --restart
# Update health check interval (ms)
llamacpp router config --health-interval 3000 --restart
# Change bind address (for remote access)
llamacpp router config --host 0.0.0.0 --restart
# Enable verbose logging (saves detailed JSON logs)
llamacpp router config --verbose true --restart
# Disable verbose logging
llamacpp router config --verbose false --restartNote: Changes require a restart to take effect. Use --restart flag to apply immediately.
The router uses separate log streams for different purposes (nginx-style):
| Log File | Purpose | Content |
|---|---|---|
router.stdout |
Request activity | Model routing, status codes, timing, prompts |
router.stderr |
System messages | Startup, shutdown, errors, proxy failures |
router.log |
Structured JSON | Detailed entries for programmatic parsing (verbose mode) |
View recent logs:
# Show activity logs (default - stdout)
llamacpp router logs
# Show system logs (errors, startup messages)
llamacpp router logs --stderr
# Follow activity in real-time
llamacpp router logs --follow
# Show last 10 lines
llamacpp router logs --lines 10Log formats:
Activity logs (stdout):
200 POST /v1/chat/completions → llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf (127.0.0.1:9001) 1234ms | "What is..."
404 POST /v1/chat/completions → unknown-model 3ms | "test" | Error: No server found
System logs (stderr):
[Router] Listening on http://127.0.0.1:9100
[Router] PID: 12345
[Router] Proxy request failed: ECONNREFUSED
Verbose JSON logs (router.log) - enable with --verbose true:
llamacpp router logs --verboseLog management:
# Clear activity log
llamacpp router logs --clear
# Clear all router logs (stdout, stderr, verbose)
llamacpp router logs --clear-all
# Rotate log files with timestamp
llamacpp router logs --rotate
# View system logs instead of activity
llamacpp router logs --stderrWhat's logged (activity):
- ✅ Model name used
- ✅ HTTP status code (color-coded)
- ✅ Request duration (ms)
- ✅ Backend server (host:port)
- ✅ First 50 chars of prompt
- ✅ Error messages (if failed)
Verbose mode benefits:
- Detailed JSON logs for LLM/script parsing
- Stored in
~/.llamacpp/logs/router.log - Automatic rotation when exceeding 100MB
- Machine-readable format with timestamps
- Router receives request with
modelfield - Finds running server configured for that model
- Proxies request to backend server
- Streams response back to client
If the requested model's server is not running, the router returns a 503 error with a helpful message.
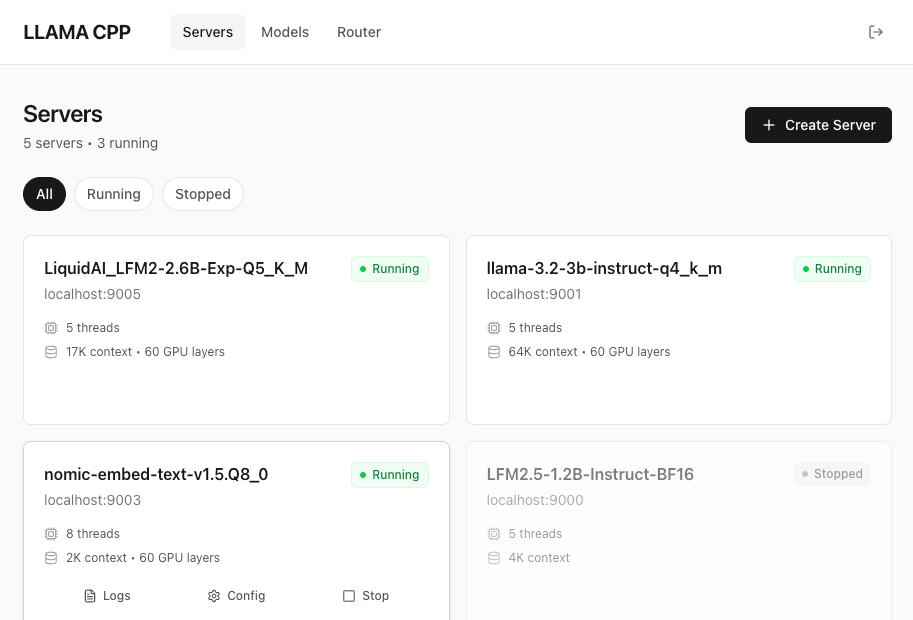
The admin interface provides full remote management of llama.cpp servers through both a REST API and a modern web UI. Perfect for programmatic control, automation, and browser-based management.
# Start the admin service (generates API key automatically)
llamacpp admin start
# View status and API key
llamacpp admin status
# Access web UI
open http://localhost:9200llamacpp admin start # Start admin service
llamacpp admin stop # Stop admin service
llamacpp admin status # Show status and API key
llamacpp admin restart # Restart service
llamacpp admin config # Update settings (--port, --host, --regenerate-key, --verbose)
llamacpp admin logs # View admin logs (with --follow, --clear, --rotate options)The Admin API provides full CRUD operations for servers and models via HTTP.
Base URL: http://localhost:9200
Authentication: Bearer token (API key auto-generated on first start)
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /api/servers |
List all servers with status |
| GET | /api/servers/:id |
Get server details |
| POST | /api/servers |
Create new server |
| PATCH | /api/servers/:id |
Update server config |
| DELETE | /api/servers/:id |
Remove server |
| POST | /api/servers/:id/start |
Start stopped server |
| POST | /api/servers/:id/stop |
Stop running server |
| POST | /api/servers/:id/restart |
Restart server |
| GET | /api/servers/:id/logs?type=stdout|stderr&lines=100 |
Get server logs |
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /api/models |
List available models |
| GET | /api/models/:name |
Get model details |
| DELETE | /api/models/:name?cascade=true |
Delete model (cascade removes servers) |
| GET | /api/models/search?q=query |
Search HuggingFace |
| POST | /api/models/download |
Download model from HF |
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /health |
Health check (no auth) |
| GET | /api/status |
System status |
Create a server:
curl -X POST http://localhost:9200/api/servers \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf",
"port": 9001,
"threads": 8,
"ctxSize": 8192
}'Start a server:
curl -X POST http://localhost:9200/api/servers/llama-3-2-3b/start \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"List all servers:
curl http://localhost:9200/api/servers \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"Delete model with cascade:
curl -X DELETE "http://localhost:9200/api/models/llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf?cascade=true" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"The web UI provides a modern, browser-based interface for managing servers and models.
Access: http://localhost:9200 (same port as API)
Features:
- Dashboard - System overview with stats and running servers
- Servers Page - Full CRUD operations (create, start, stop, restart, delete)
- Models Page - Browse models, view usage, delete with cascade
- Real-time updates - Auto-refresh every 5 seconds
- Dark theme - Modern, clean interface
Pages:
| Page | Path | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Dashboard | /dashboard |
System overview and quick stats |
| Servers | /servers |
Manage all servers (list, start/stop, configure) |
| Models | /models |
Browse models, view server usage, delete |
Building Web UI:
The web UI is built with React + Vite + TypeScript. To build:
cd web
npm install
npm run buildThis generates static files in web/dist/ which are automatically served by the admin service.
Development:
cd web
npm install
npm run dev # Starts dev server on localhost:5173 with API proxySee web/README.md for detailed web development documentation.
Configure the admin service with various options:
# Change port
llamacpp admin config --port 9300 --restart
# Enable remote access (WARNING: security implications)
llamacpp admin config --host 0.0.0.0 --restart
# Regenerate API key (invalidates old key)
llamacpp admin config --regenerate-key --restart
# Enable verbose logging
llamacpp admin config --verbose true --restartNote: Changes require a restart to take effect. Use --restart flag to apply immediately.
Default Security Posture:
- Host:
127.0.0.1(localhost only - secure by default) - API Key: Auto-generated 32-character hex string
- Storage: API key stored in
~/.llamacpp/admin.json(file permissions 600)
Remote Access:
0.0.0.0 allows remote access from your network and potentially the internet.
If you need remote access:
# Enable remote access
llamacpp admin config --host 0.0.0.0 --restart
# Ensure you use strong API key
llamacpp admin config --regenerate-key --restartBest Practices:
- Keep default
127.0.0.1for local development - Use HTTPS reverse proxy (nginx/Caddy) for remote access
- Rotate API keys regularly if exposed
- Monitor admin logs for suspicious activity
The admin service maintains separate log streams:
| Log File | Purpose | Content |
|---|---|---|
admin.stdout |
Request activity | Endpoint, status, duration |
admin.stderr |
System messages | Startup, shutdown, errors |
View logs:
# Show activity logs (default - stdout)
llamacpp admin logs
# Show system logs (errors, startup)
llamacpp admin logs --stderr
# Follow in real-time
llamacpp admin logs --follow
# Clear all logs
llamacpp admin logs --clear
# Rotate logs with timestamp
llamacpp admin logs --rotateStarting the admin service:
$ llamacpp admin start
✓ Admin service started successfully!
Port: 9200
Host: 127.0.0.1
API Key: a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8i9j0k1l2m3n4o5p6
API: http://localhost:9200/api
Web UI: http://localhost:9200
Health: http://localhost:9200/health
Quick Commands:
llamacpp admin status # View status
llamacpp admin logs -f # Follow logs
llamacpp admin config --help # Configure options
Admin status:
$ llamacpp admin status
Admin Service Status
────────────────────
Status: ✅ RUNNING
PID: 98765
Uptime: 2h 15m
Port: 9200
Host: 127.0.0.1
API Key: a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8i9j0k1l2m3n4o5p6
API: http://localhost:9200/api
Web UI: http://localhost:9200
Configuration:
Config: ~/.llamacpp/admin.json
Plist: ~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.llama.admin.plist
Logs: ~/.llamacpp/logs/admin.{stdout,stderr}
Quick Commands:
llamacpp admin stop # Stop service
llamacpp admin restart # Restart service
llamacpp admin logs -f # Follow logs
Creating a server:
$ llamacpp server create llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf
✓ Server created and started successfully!
Model: llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf
Port: 9000
Status: Running (PID 12345)
API endpoint: http://localhost:9000
Viewing running servers:
$ llamacpp ps
┌─────────────────────────┬──────┬────────────┬──────┬──────────┬────────┐
│ SERVER ID │ PORT │ STATUS │ PID │ MEMORY │ UPTIME │
├─────────────────────────┼──────┼────────────┼──────┼──────────┼────────┤
│ llama-3-2-3b-instruct │ 9000 │ ✅ RUNNING │ 1234 │ 594.0 MB │ 15m │
│ qwen2-7b-instruct-q4-k │ 9001 │ ✅ RUNNING │ 5678 │ 1.2 GB │ 2h │
└─────────────────────────┴──────┴────────────┴──────┴──────────┴────────┘
Total: 2 servers (2 running, 0 stopped)
Running interactive chat:
$ llamacpp server run llama-3.2-3b
Connected to llama-3.2-3b-instruct on port 9000
You: What is the capital of France?
Assistant: The capital of France is Paris...
You: exit
One-shot message:
$ llamacpp server run llama-3.2-3b -m "What is the capital of France?"
Assistant: The capital of France is Paris...
Launch the interactive TUI dashboard for monitoring and managing servers.
llamacppSee Interactive TUI for full details.
List all GGUF models in ~/models directory.
llamacpp lsSearch Hugging Face for GGUF models.
# Search for models
llamacpp search "llama 3.2"
# Limit results
llamacpp search "qwen" --limit 10
# Show files for a specific result (by index number)
llamacpp search "llama 3b" --files 1Options:
-l, --limit <number>- Max results to show (default: 20)--files [number]- Show available GGUF files for result # (e.g., --files 1)
Tip: Results are numbered. Use the number with --files to see available quantizations for that model!
Show details about a model or file without downloading.
# Show model info and all GGUF files
llamacpp show bartowski/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-GGUF
# Show info for a specific file
llamacpp show bartowski/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-GGUF/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf
# Or use --file flag
llamacpp show bartowski/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-GGUF --file Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.ggufOptions:
-f, --file <filename>- Show details for a specific file
Displays: Downloads, likes, license, tags, and available GGUF files
Download a GGUF model from Hugging Face.
# Option 1: Full path (recommended)
llamacpp pull bartowski/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-GGUF/llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf
# Option 2: Repo + --file flag
llamacpp pull bartowski/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-GGUF --file llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.ggufOptions:
-f, --file <filename>- Specific GGUF file (alternative to path)
Delete a model file from ~/models (and stop any associated servers).
llamacpp rm llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf
llamacpp rm llama-3.2 # Partial name matchingList all servers with status, memory usage, and uptime.
llamacpp psShows:
- Server ID and model name
- Port number
- Status (running/stopped/crashed)
- Process ID (PID)
- Memory usage (RAM consumption)
- Uptime (how long server has been running)
View log sizes for all servers and perform batch log operations.
# Show table of log sizes for all servers
llamacpp logs
# Clear current logs for ALL servers (preserves archives)
llamacpp logs --clear
# Delete only archived logs for ALL servers (preserves current)
llamacpp logs --clear-archived
# Clear current + delete ALL archived logs (maximum cleanup)
llamacpp logs --clear-all
# Rotate ALL server logs with timestamps
llamacpp logs --rotateDisplays:
- Current stderr size per server
- Current stdout size per server
- Archived logs size and count
- Total log usage per server
- Grand total across all servers
Batch Operations:
--clear- Truncates all current logs to 0 bytes (archives preserved)--clear-archived- Deletes only archived logs (current logs preserved)--clear-all- Clears current AND deletes all archives (frees maximum space)--rotate- Archives all current logs with timestamps
Use case: Quickly see which servers are accumulating large logs, or clean up all logs at once.
Create and start a new llama-server instance.
llamacpp server create llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf
llamacpp server create llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf --port 8080 --ctx-size 16384 --verbose
# Enable remote access (WARNING: security implications)
llamacpp server create llama-3.2-3b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf --host 0.0.0.0Options:
-p, --port <number>- Port number (default: auto-assign from 9000)-h, --host <address>- Bind address (default:127.0.0.1for localhost only, use0.0.0.0for remote access)-t, --threads <number>- Thread count (default: half of CPU cores)-c, --ctx-size <number>- Context size (default: based on model size)-g, --gpu-layers <number>- GPU layers (default: 60)-v, --verbose- Enable verbose HTTP logging (default: enabled)
--host 0.0.0.0 binds the server to all network interfaces, allowing remote access from your local network and potentially the internet. Only use this if you understand the security implications and need remote access. For local development, keep the default 127.0.0.1 (localhost only).
Show detailed configuration and status information for a server.
llamacpp server show llama-3.2-3b # By partial name
llamacpp server show 9000 # By port
llamacpp server show llama-3-2-3b # By server IDDisplays:
- Server ID, model name, and path
- Current status (running/stopped/crashed)
- Host and port
- PID (process ID)
- Runtime info (uptime, memory usage)
- Configuration (host, threads, context size, GPU layers, verbose logging)
- Timestamps (created, last started/stopped)
- System paths (plist file, log files)
- Quick commands for common next actions
Identifiers: Port number, server ID, partial model name
Update server configuration parameters without recreating the server.
# Change model while keeping all other settings
llamacpp server config llama-3.2-3b --model llama-3.2-1b-instruct-q4_k_m.gguf --restart
# Update context size and restart
llamacpp server config llama-3.2-3b --ctx-size 8192 --restart
# Update threads without restarting
llamacpp server config 9000 --threads 8
# Enable remote access (WARNING: security implications)
llamacpp server config llama-3.2-3b --host 0.0.0.0 --restart
# Toggle verbose logging
llamacpp server config llama-3.2-3b --no-verbose --restart
# Update multiple parameters
llamacpp server config llama-3.2-3b --threads 8 --ctx-size 16384 --gpu-layers 40 --restartOptions:
-m, --model <filename>- Update model (filename or path)-h, --host <address>- Update bind address (127.0.0.1for localhost,0.0.0.0for remote access)-t, --threads <number>- Update thread count-c, --ctx-size <number>- Update context size-g, --gpu-layers <number>- Update GPU layers-v, --verbose- Enable verbose logging--no-verbose- Disable verbose logging-r, --restart- Automatically restart server if running
Note: Changes require a server restart to take effect. Use --restart to automatically stop and start the server with the new configuration.
--host 0.0.0.0 binds the server to all network interfaces, allowing remote access. Only use this if you understand the security implications.
Identifiers: Port number, server ID, partial model name
Start an existing stopped server.
llamacpp server start llama-3.2-3b # By partial name
llamacpp server start 9000 # By port
llamacpp server start llama-3-2-3b # By server IDIdentifiers: Port number, server ID, partial model name, or model filename
Run an interactive chat session with a model, or send a single message.
# Interactive mode (REPL)
llamacpp server run llama-3.2-3b # By partial name
llamacpp server run 9000 # By port
llamacpp server run llama-3-2-3b # By server ID
# One-shot mode (single message and exit)
llamacpp server run llama-3.2-3b -m "What is the capital of France?"
llamacpp server run 9000 --message "Explain quantum computing in simple terms"Options:
-m, --message <text>- Send a single message and exit (non-interactive mode)
Identifiers: Port number, server ID, partial model name, or model filename
In interactive mode, type exit or press Ctrl+C to end the session.
Stop a running server by model name, port, or ID.
llamacpp server stop llama-3.2-3b
llamacpp server stop 9000Remove a server configuration and launchctl service (preserves model file).
llamacpp server rm llama-3.2-3b
llamacpp server rm 9000View server logs with smart filtering.
Default (verbose enabled):
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b
# Output: 2025-12-09 18:02:23 POST /v1/chat/completions 127.0.0.1 200 "What is..." 305 22 1036Without --verbose on server:
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b
# Output: Only internal server logs (cache, slots) - no HTTP request logsMore examples:
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --http
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --follow
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --lines 100
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --errors
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --verbose
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --filter "error|warning"
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --clear
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --clear-archived
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --clear-all
llamacpp server logs llama-3.2-3b --rotate
**Options:**
- `-f, --follow` - Follow log output in real-time
- `-n, --lines <number>` - Number of lines to show (default: 50)
- `--http` - Show full HTTP JSON request/response logs
- `--errors` - Show only error messages
- `--verbose` - Show all messages including debug internals
- `--filter <pattern>` - Custom grep pattern for filtering
- `--stdout` - Show stdout instead of stderr (rarely needed)
- `--clear` - Clear (truncate) log file to zero bytes
- `--clear-archived` - Delete only archived logs (preserves current logs)
- `--clear-all` - Clear current logs AND delete all archived logs (frees most space)
- `--rotate` - Rotate log file with timestamp (e.g., `server.2026-01-22-19-30-00.stderr`)
**Automatic Log Rotation:**
Logs are automatically rotated when they exceed 100MB during:
- `llamacpp server start <identifier>` - Rotates before starting
- `llamacpp server config <identifier> --restart` - Rotates before restarting
Rotated logs are saved with timestamps in the same directory: `~/.llamacpp/logs/`
**Output Formats:**
Default compact format:
TIMESTAMP METHOD ENDPOINT IP STATUS "MESSAGE..." TOKENS_IN TOKENS_OUT TIME_MS
The compact format shows one line per HTTP request and includes:
- User's message (first 50 characters)
- Token counts (prompt tokens in, completion tokens out)
- Total response time in milliseconds
**Note:** Verbose logging is now enabled by default. HTTP request logs are available by default.
Use `--http` to see full request/response JSON, or `--verbose` option to see all internal server logs.
## Configuration
llamacpp-cli stores its configuration in `~/.llamacpp/`:
~/.llamacpp/ ├── config.json # Global settings ├── router.json # Router configuration ├── admin.json # Admin service configuration (includes API key) ├── servers/ # Server configurations │ └── .json ├── logs/ # Server logs │ ├── .stdout │ ├── .stderr │ ├── router.{stdout,stderr,log} │ └── admin.{stdout,stderr} └── history/ # Historical metrics (TUI) └── .json
## Smart Defaults
llamacpp-cli automatically configures optimal settings based on model size:
| Model Size | Context Size | Threads | GPU Layers |
|------------|--------------|---------|------------|
| < 1GB | 2048 | Half cores | 60 |
| 1-3GB | 4096 | Half cores | 60 |
| 3-6GB | 8192 | Half cores | 60 |
| > 6GB | 16384 | Half cores | 60 |
All servers include `--embeddings` and `--jinja` flags by default.
## How It Works
llamacpp-cli uses macOS launchctl to manage llama-server processes:
1. Creates a launchd plist file in `~/Library/LaunchAgents/`
2. Registers the service with `launchctl load`
3. Starts the server with `launchctl start`
4. Monitors status via `launchctl list` and `lsof`
Services are named `com.llama.<model-id>`.
**Auto-Restart Behavior:**
- When you **start** a server, it's registered with launchd and will auto-restart on crash
- When you **stop** a server, it's unloaded from launchd and stays stopped (no auto-restart)
- Crashed servers will automatically restart (when loaded)
**Router and Admin Services:**
- The **Router** (`com.llama.router`) provides a unified OpenAI-compatible endpoint for all models
- The **Admin** (`com.llama.admin`) provides REST API + web UI for remote management
- Both run as launchctl services similar to individual model servers
## Known Limitations
- **macOS only** - Relies on launchctl for service management (Linux/Windows support planned)
- **Homebrew dependency** - Requires llama.cpp installed via `brew install llama.cpp`
- **~/models convention** - Expects GGUF models in `~/models` directory
- **Single binary** - Assumes llama-server at `/opt/homebrew/bin/llama-server`
- **Port range** - Auto-assignment limited to 9000-9999 (configurable with `--port`)
## Troubleshooting
### Command not found
Make sure npm global bin directory is in your PATH:
```bash
npm config get prefix # Should be in PATH
Install llama.cpp via Homebrew:
brew install llama.cppllamacpp-cli will automatically find the next available port. Or specify a custom port:
llamacpp server create model.gguf --port 8080Check the logs for errors:
llamacpp server logs <identifier> --errorsCheck that static files are built:
cd web
npm install
npm run buildThen restart the admin service:
llamacpp admin restartGet your current API key:
llamacpp admin status # Shows API keyOr regenerate a new one:
llamacpp admin config --regenerate-key --restart# Install dependencies
npm install
# Run in development mode
npm run dev # Launch TUI
npm run dev -- ps # List servers (static table)
npm run dev -- ls # List models
# Build for production
npm run build
# Clean build artifacts
npm run clean# Navigate to web directory
cd web
# Install dependencies
npm install
# Run dev server (with API proxy to localhost:9200)
npm run dev
# Build for production
npm run build
# Clean build artifacts
rm -rf distThe web UI dev server runs on http://localhost:5173 with automatic API proxying to the admin service. See web/README.md for detailed documentation.
This project uses commit-and-tag-version for automated releases based on conventional commits.
Commit Message Format:
# Features (bumps minor version)
git commit -m "feat: add interactive chat command"
git commit -m "feat(search): add limit option for search results"
# Bug fixes (bumps patch version)
git commit -m "fix: handle port conflicts correctly"
git commit -m "fix(logs): stream logs without buffering"
# Breaking changes (bumps major version)
git commit -m "feat!: change server command structure"
git commit -m "feat: major refactor
BREAKING CHANGE: server commands now require 'server' prefix"
# Other types (no version bump, hidden in changelog)
git commit -m "chore: update dependencies"
git commit -m "docs: fix typo in README"
git commit -m "test: add unit tests for port manager"Release Commands:
# Automatic version bump based on commits
npm run release
# Force specific version bump
npm run release:patch # 1.0.0 → 1.0.1
npm run release:minor # 1.0.0 → 1.1.0
npm run release:major # 1.0.0 → 2.0.0
# First release (doesn't bump version, just tags)
npm run release:firstWhat happens during release:
- Analyzes commits since last release
- Determines version bump (feat = minor, fix = patch, BREAKING CHANGE = major)
- Updates
package.jsonversion - Generates/updates
CHANGELOG.md - Creates git commit:
chore(release): v1.2.3 - Creates git tag:
v1.2.3 - Pushes tags to GitHub
- Publishes to npm with
--access public
Contributions are welcome! If you'd like to contribute:
- Open an issue first for major changes to discuss the approach
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature) - Make your changes and test with
npm run dev - Commit using conventional commits (see Releasing section)
feat:for new featuresfix:for bug fixesdocs:for documentationchore:for maintenance
- Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/amazing-feature) - Open a Pull Request
CLI Development:
- Use
npm run dev -- <command>to test commands without building - Check logs with
llamacpp server logs <server> --errorswhen debugging - Test launchctl integration with
launchctl list | grep com.llama - All server configs are in
~/.llamacpp/servers/ - Test interactive chat with
npm run dev -- server run <model>
Web UI Development:
- Navigate to
web/directory and runnpm run devfor hot reload - API proxy automatically configured for
localhost:9200 - Update types in
web/src/types/api.tswhen API changes - Build with
npm run buildand test with admin service - See
web/README.mdfor detailed web development guide
Built on top of the excellent llama.cpp project by Georgi Gerganov and contributors.
MIT