Stop just unlocking the UI. Start proving the identity.
Typical biometric plugins (such as local_auth) return only a boolean indicating whether authentication succeeded.
biometric_signature goes significantly further by generating a verifiable cryptographic signature using a private key stored in hardware (Secure Enclave / StrongBox).
Even if an attacker bypasses or hooks biometric APIs, your backend will still reject the request because the attacker cannot forge a hardware-backed signature without the private key.
-
Cryptographic Proof Of Identity: Hardware-backed RSA or ECDSA signatures that your backend can independently verify.
-
Decryption Support:
- RSA: RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding (Android + iOS)
- EC: ECIES (X9.63 → SHA-256 → AES-GCM)
-
Hardware Security: Uses Secure Enclave (iOS) and Keystore/StrongBox (Android).
-
Hybrid Architectures:
-
Android Hybrid EC:
Hardware EC signing + software ECIES decryption. The software EC private key is AES-wrapped using a StrongBox/Keystore AES-256 master key that requires biometric authentication for every unwrap.
-
iOS Hybrid RSA:
Hardware EC signing + software RSA decryption key. The RSA key is encrypted using ECIES with Secure Enclave EC public key material.
-
Key Invalidation: Keys can be bound to biometric enrollment state (fingerprint/Face ID changes).
-
Device Credentials: Optional PIN/Pattern/Password fallback on Android.
The plugin supports three secure operational modes:
- RSA Mode:
- RSA-2048 signing (always hardware-backed)
- Optional RSA decryption
- Private key never leaves secure hardware
- EC Signing-Only:
- Hardware-backed P-256 key
- ECDSA signing only
- No decryption support
- Hybrid EC Mode: Combines hardware signing with software decryption keys:
- Android:
- Hardware EC key for signing
- Software EC key for ECIES decryption
- Software EC private key encrypted using:
- AES-256 GCM master key stored in Keystore/StrongBox
- Per-operation biometric authentication required
- Wrapped EC private key blob stored in app-private files (MODE_PRIVATE)
- Public EC key also stored in app-private files
- iOS:
- Hardware EC key for signing
- Software RSA key for PKCS#1 decryption
- RSA private key is wrapped using ECIES with Secure Enclave EC public key
- Wrapped RSA key stored in Keychain as
kSecClassGenericPassword
- Android:
-
Enrollment
User authenticates → hardware generates a signing key.
Hybrid modes additionally generate a software decryption key, which is then encrypted using secure hardware.
-
Signing
Biometric prompt is shown
Hardware unlocks the signing key, and a verifiable signature is produced.
-
Decryption
A biometric prompt is shown again.
Hybrid modes unwrap the software private key using hardware-protected AES-GCM, then decrypt the payload.
-
Backend Verification
The backend verifies signatures using the registered public key.
Verification must not be performed on the client.
Perform verification on the server. Below are reference implementations.
const crypto = require('crypto');
function verifySignature(publicKeyPem, payload, signatureBase64) {
const verify = crypto.createVerify('SHA256');
verify.update(payload); // The original string you sent to the plugin
verify.end();
// Returns true if valid
return verify.verify(publicKeyPem, Buffer.from(signatureBase64, 'base64'));
}from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import padding
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization
import base64
def verify_signature(public_key_pem_str, payload_str, signature_base64_str):
public_key = serialization.load_pem_public_key(public_key_pem_str.encode())
signature = base64.b64decode(signature_base64_str)
try:
# Assuming RSA (For EC, use ec.ECDSA(hashes.SHA256()))
public_key.verify(
signature,
payload_str.encode(),
padding.PKCS1v15(),
hashes.SHA256()
)
return True
except Exception:
return Falseimport (
"crypto"
"crypto/rsa"
"crypto/sha256"
"crypto/x509"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/pem"
"fmt"
)
func verify(pubPemStr, payload, sigBase64 string) error {
block, _ := pem.Decode([]byte(pubPemStr))
pub, _ := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(block.Bytes)
rsaPub := pub.(*rsa.PublicKey)
hashed := sha256.Sum256([]byte(payload))
sig, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(sigBase64)
return rsa.VerifyPKCS1v15(rsaPub, crypto.SHA256, hashed[:], sig)
}To get started with Biometric Signature, follow these steps:
- Add the package to your project by including it in your
pubspec.yamlfile:
dependencies:
biometric_signature: ^8.4.0| Android | iOS | |
|---|---|---|
| Support | SDK 24+ | 13.0+ |
This plugin works with Touch ID or Face ID. To use Face ID in available devices, you need to add:
<dict>
<key>NSFaceIDUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app is using FaceID for authentication</string>
</dict>to your Info.plist file.
This plugin requires the use of a FragmentActivity as opposed to Activity. This can be easily done by switching to use FlutterFragmentActivity as opposed to FlutterActivity in your manifest or your own Activity class if you are extending the base class.
Update your project's AndroidManifest.xml file to include the
USE_BIOMETRIC permission.
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.app">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.USE_BIOMETRIC" />
</manifest>- Import the package in your Dart code:
import 'package:biometric_signature/biometric_signature.dart';
import 'package:biometric_signature/android_config.dart';
import 'package:biometric_signature/ios_config.dart';
import 'package:biometric_signature/signature_options.dart';
import 'package:biometric_signature/decryption_options.dart';- Initialize the Biometric Signature instance:
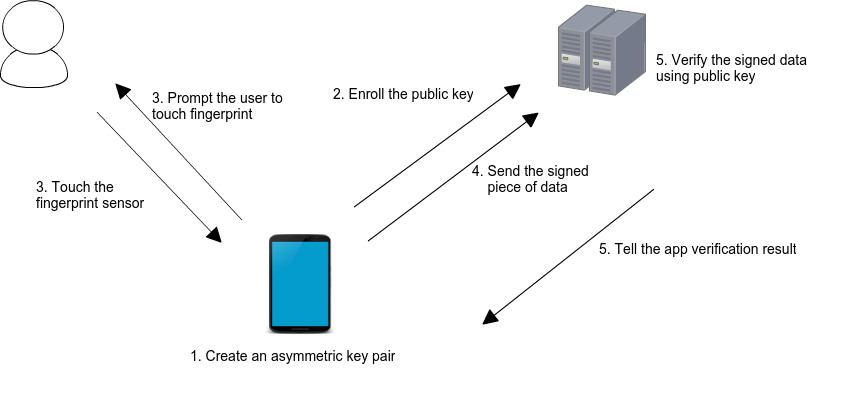
final biometricSignature = BiometricSignature();This package simplifies server authentication using biometrics. The following image from Android Developers Blog illustrates the basic use case:
When a user enrolls in biometrics, a key pair is generated. The private key is securely stored on the device, while the public key is sent to a server for registration. To authenticate, the user is prompted to use their biometrics, unlocking the private key. A cryptographic signature is then generated and sent to the server for verification. If the server successfully verifies the signature, it returns an appropriate response, authorizing the user.
This class provides methods to manage and utilize biometric authentication for secure server interactions. It supports both Android and iOS platforms.
Generates a new key pair (RSA 2048 or EC) for biometric authentication. The private key is securely stored on the device, while the KeyCreationResult returned from this call contains a FormattedValue with the public key in the requested representation. StrongBox support is available for compatible Android devices and Secure Enclave support is available for iOS.
Hybrid modes generate both hardware and software keys, encrypting software keys via secure hardware.
-
Parameters: -
androidConfig: AnAndroidConfigobject containing following properties: -useDeviceCredentials: Aboolto indicate whether Device Credentials' fallback support is needed for the compatible Android devices. -signatureType: An enum value ofAndroidSignatureType. -setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollment(optional): Aboolto indicate whether the key should be invalidated when a new biometric is enrolled. Defaults totrue. When set totrue, adding a new fingerprint, face, or iris will invalidate the existing key, requiring re-enrollment. This enhances security by ensuring keys are tied to the specific biometric set at creation time. -enableDecryption(optional): Aboolto indicate whether the generated key should support decryption (RSA only). Defaults tofalse.iosConfig: AnIosConfigobject containing following properties:useDeviceCredentials: Aboolto indicate whether Device Credentials' fallback support is needed.signatureType: An enum value ofIOSSignatureType.biometryCurrentSet(optional): Aboolto constrain key usage to the current biometric enrollment. Defaults totrue. When set totrue, the key is bound to the current set of enrolled biometrics. If biometrics are changed (e.g., a new fingerprint is added or removed), the key becomes invalid, requiring re-enrollment.
keyFormat(optional): AKeyFormatvalue describing how the public key should be returned. Defaults toKeyFormat.base64for backward compatibility.enforceBiometric(optional): Aboolto require biometric authentication before generating the key-pair. Defaults tofalse. When set totrue, the user will be prompted for biometric authentication (fingerprint, face, or iris) before the key-pair is generated. This ensures that the person holding the device is verified before keys are created, adding an extra layer of security for sensitive use cases.
-
Returns:
Future<KeyCreationResult?>. Access the formatted public key throughresult.publicKey, e.g.:
final keyResult = await biometricSignature.createKeys(keyFormat: KeyFormat.pem);
final pem = keyResult?.publicKey.asString();
final derBytes = keyResult?.publicKey.toBytes();- Error Codes:
AUTH_FAILED: Error generating keys.
Prompts the user for biometric authentication and generates a cryptographic signature (RSA PKCS#1v1.5 SHA-256 or ECDSA P-256) using the securely stored private key. The new response is a SignatureResult that carries both the signature and public key in the requested output format.
Hybrid modes always sign using the hardware EC key.
-
Parameters:
options: ASignatureOptionsinstance that specifies:payload(required): The UTF-8 payload to sign.promptMessage(optional): Message displayed in the biometric prompt. Default toAuthenticate.androidOptions(optional): AnAndroidSignatureOptionsobject offering:cancelButtonText: Overrides the cancel button label. Defaults toCancel.allowDeviceCredentials: Enables device-credential fallback on compatible Android devices.subtitle: Optional secondary text displayed under the prompt title on Android.
iosOptions(optional): AnIosSignatureOptionsobject offering:shouldMigrate: Triggers migration from pre-5.x Keychain storage to Secure Enclave.
keyFormat(optional): Preferred output format (KeyFormat.base64by default). This is a new parameter.
-
Returns:
Future<SignatureResult?>. Use theFormattedValuehelpers to obtain the representation you need:
final signatureResult = await biometricSignature.createSignature(
SignatureOptions(
payload: 'Payload to sign',
keyFormat: KeyFormat.raw,
promptMessage: 'Authenticate to Sign',
androidOptions: const AndroidSignatureOptions(allowDeviceCredentials: false),
iosOptions: const IosSignatureOptions(shouldMigrate: false),
),
);
final Uint8List rawSignature = signatureResult!.signature.toBytes();
final String base64Signature = signatureResult.signature.toBase64();- Error Codes:
INVALID_PAYLOAD: Payload is required and must be valid UTF-8.AUTH_FAILED: Error generating the signature.
KeyFormat lets you decide how both the public key and signature are returned:
KeyFormat.base64— URL/transport friendly string (default).KeyFormat.pem— PEM block with headers, using SubjectPublicKeyInfo on both platforms.KeyFormat.raw—Uint8List(DER bytes for public keys, raw signature bytes).KeyFormat.hex— Lowercase hexadecimal string.
Each FormattedValue exposes helpers such as toBase64(), toBytes(), toHex() and asString() so you can easily convert between representations.
Decrypts the given payload using the private key and biometrics. Supports both RSA (PKCS#1) and EC (ECIES with P-256 → ECDH → X9.63 KDF (SHA-256) → AES-128-GCM) decryption.
-
Parameters:
options: ADecryptionOptionsinstance that specifies:payload(required): The Base64 encoded encrypted payload to decrypt.promptMessage(optional): Message displayed in the biometric prompt. Defaults toAuthenticate.androidOptions(optional): AnAndroidDecryptionOptionsobject offering:cancelButtonText: Overrides the cancel button label. Defaults toCancel.allowDeviceCredentials: Enables device-credential fallback on compatible Android devices.subtitle: Optional secondary text displayed under the prompt title on Android.
iosOptions(optional): AnIosDecryptionOptionsobject offering:shouldMigrate: Triggers migration from pre-5.x Keychain storage to Secure Enclave.
-
Returns:
Future<DecryptResult?>. TheDecryptResultcontains thedecryptedDatastring. -
Supported Algorithms:
- RSA: Uses RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding (Android & iOS Hybrid mode)
- EC: Uses ECIES (Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme) with:
- Curve: P-256 (secp256r1)
- Key Agreement: ECDH
- KDF: ANSI X9.63 with SHA-256
- Encryption: AES-128-GCM (12-byte IV, 128-bit auth tag)
-
Native Architecture Summary:
- Android:
- Hardware EC/RSA keys for signing (Keystore/StrongBox)
- Software EC key for ECIES decryption
- Wrapped EC private key stored in app-private files
- Unwrapped at runtime using biometric-protected AES-256 master key
- Manual ECIES implementation: ECDH → X9.63 KDF → AES-GCM
- All sensitive material zeroized immediately after use
- iOS:
- Secure Enclave EC key for signing
- Native ECIES using
SecKeyAlgorithm.eciesEncryptionStandardX963SHA256AESGCM - Hybrid RSA mode: software RSA key wrapped via ECIES, stored in Keychain
- Android:
// RSA Decryption Example
final decryptResult = await biometricSignature.decrypt(
DecryptionOptions(
payload: 'Base64 Encrypted RSA Payload',
promptMessage: 'Authenticate to Decrypt',
androidOptions: const AndroidDecryptionOptions(allowDeviceCredentials: false),
iosOptions: const IosDecryptionOptions(shouldMigrate: false),
),
);
// EC Decryption Example (ECIES)
final ecDecryptResult = await biometricSignature.decrypt(
DecryptionOptions(
payload: 'Base64 Encrypted ECIES Payload',
promptMessage: 'Authenticate to Decrypt',
androidOptions: const AndroidDecryptionOptions(allowDeviceCredentials: false),
iosOptions: const IosDecryptionOptions(shouldMigrate: false),
),
);
final decryptedString = decryptResult?.decryptedData;- Error Codes:
INVALID_PAYLOAD: Payload is required or invalid format.AUTH_FAILED: Error decrypting the payload or authentication failed.
Deletes all key material (hardware + hybrid). Hybrid wrapped keys stored in Keystore are also removed.
-
Returns:
bool-trueif the key(s) was successfully deleted. -
Error Codes:
-
AUTH_FAILED: Error deleting the biometric key
Checks if biometric authentication is available on the device. On Android, it specifically checks for Biometric Strong Authenticators, which provide a higher level of security.
-
Returns:
String- The type of biometric authentication available (fingerprint,face,iris,TouchID,FaceID, orbiometric) or a string indicating the error if no biometrics are available. -
Possible negative returns in Android:
-
none, BIOMETRIC_ERROR_NO_HARDWARE: No biometric hardware available. -
none, BIOMETRIC_ERROR_HW_UNAVAILABLE: Biometric hardware currently unavailable. -
none, BIOMETRIC_ERROR_NONE_ENROLLED: No biometric credentials enrolled. -
none, BIOMETRIC_ERROR_SECURITY_UPDATE_REQUIRED: Security update required. -
none, BIOMETRIC_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED: Biometric authentication is unsupported. -
none, BIOMETRIC_STATUS_UNKNOWN: Unknown status. -
none, NO_BIOMETRICS: No biometrics.
Checks if the biometric key pair exists on the device. Optionally, it can also verify the validity of the key by attempting to initialize a signature with it. Since the key requires that user authentication takes place for every use of the key, it is also irreversibly invalidated once a new biometric is enrolled or once no more biometrics are enrolled (when setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollment is true on Android or biometryCurrentSet is true on iOS).
- Parameters:
checkValidity: A bool indicating whether to check the validity of the key by initializing a signature. Default isfalse.
- Returns:
bool-trueif the key pair exists (and is valid ifcheckValidityistrue),falseotherwise. - Error Codes:
AUTH_FAILED: Error checking if the biometric key exists.
import 'package:biometric_signature/biometric_signature.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(const MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const MaterialApp(home: Scaffold(body: BiometricDemo()));
}
}
class BiometricDemo extends StatefulWidget {
const BiometricDemo({super.key});
@override
State<BiometricDemo> createState() => _BiometricDemoState();
}
class _BiometricDemoState extends State<BiometricDemo> {
final _biometricSignature = BiometricSignature();
KeyCreationResult? keyResult;
SignatureResult? signatureResult;
Future<void> _generateKeys() async {
keyResult = await _biometricSignature.createKeys(
keyFormat: KeyFormat.pem,
androidConfig: AndroidConfig(
useDeviceCredentials: false,
signatureType: AndroidSignatureType.RSA,
setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollment: true, // Key invalidated when new biometric is enrolled
enableDecryption: true, // Enable decryption support
),
iosConfig: IosConfig(
useDeviceCredentials: false,
signatureType: IOSSignatureType.RSA,
biometryCurrentSet: true, // Key constrained to current biometric enrollment
),
enforceBiometric: true, // Require biometric authentication before generating keys
);
debugPrint('Public key (${keyResult.publicKey.format.wireValue}):\n${keyResult?.publicKey.asString()}');
setState(() {});
}
Future<void> _sign() async {
signatureResult = await _biometricSignature.createSignature(
SignatureOptions(
payload: 'Payload to sign',
keyFormat: KeyFormat.base64,
promptMessage: 'Authenticate to Sign',
androidOptions: const AndroidSignatureOptions(
subtitle: 'Approve the login to continue',
allowDeviceCredentials: false,
),
iosOptions: const IosSignatureOptions(shouldMigrate: false),
),
);
debugPrint('Signature (${signatureResult.signature.format.wireValue}): ${signatureResult?.signature}');
setState(() {});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(24),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _generateKeys,
child: const Text('Create keys (PEM)'),
),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _sign,
child: const Text('Sign payload (RAW)'),
),
if (signatureResult != null) ...[
const SizedBox(height: 16),
Text('Signature HEX:\n${signatureResult!.signature.toHex()}'),
],
],
),
);
}
}