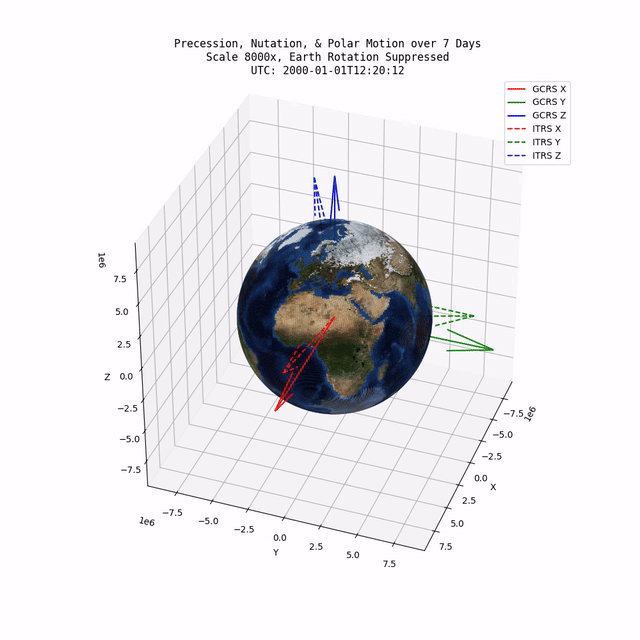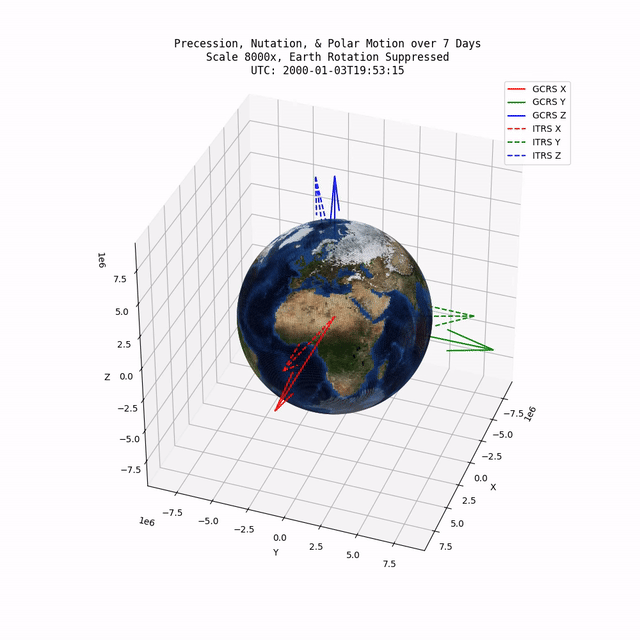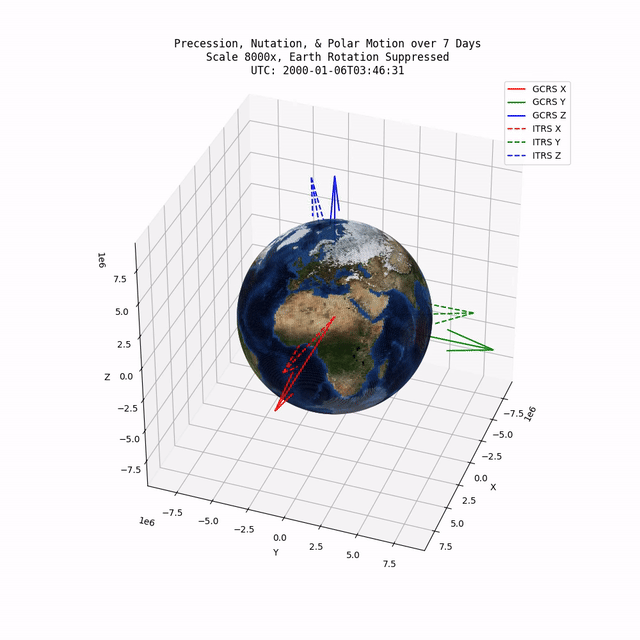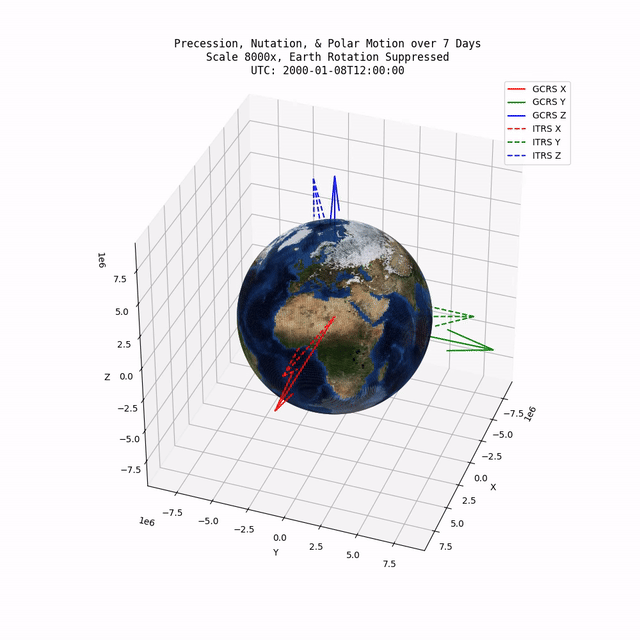
TerraFrame is a library designed to provided key Earth related calculations and associated functionality to modeling & simulation software. Primarily, TerraFrame provides Earth orientation and gravity routines.
TerraFrame provides an implementation of the IAU 2006/2000A precession-nutation model which accounts for precession, nutation, and polar motion. Specifically, this implementation provides a transformation tensor between the Geocentric Celestial Reference System (GCRS) and the International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS).
TerraFrame also provides routines for calculating the Earth's angular velocity tensor. The angular velocity tensor is based on the partial derivative of the numerous IAU 2006/2000A equations with respect to time (in seconds).
IERS precession and nutation model data files are shipped with TerraFrame. Utility code is also provided which automates the downloading of IERS data for polar motion, UTC, and UT1 offsets.
Gravity calculations are provided by an implementation of the EGM2008. A double Clenshaw summation approach is used to evaluate the spherical harmonics which yields high numerical stability and computational efficiency. TerraFrame is numerically capable of evaluating EGM2008 to it’s complete degree and order: 2190.
By default, only data for degree and order 200 is shipped with TerraFrame for space efficiency. Most near earth modeling & simulation applications will not need to exceed degree and order 100 per WGS84 guidance.
Support is provided for converting from geodetic latitude, longitude, and height above ellipsoid to geocentric cartesian coordinates or vice versa. The WGS84 spheroid and a simple spherical earth are provided as built-in options.
TerraFrame also provides robust datetime and timescale conversion functionality that is fully leap second aware. Conversions between UTC, UT1, TT, and TAI are provided. The user is encouraged to not work in UTC directly to avoid leap second ambiguity. Conversion to UTC from TT or TAI can be safely done in post-processing.
This project - except for the IERS and WGS84 data files - is covered under the Mozilla Public License Version 2.0 (MPL2). See the LICENSE.txt file for more information.
This project uses data published by the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS). The original data along with additional information can be found on the IERS website: here.
The Astropy, PyERFA, and GeographicLib libraries have been used as invaluable sources of truth for the testing of TerraFrame.
This project would not have been possible without the technical information provided by the following sources:
- Urban, S. E., & Seidelmann, P. K. (Eds.). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac (3rd ed.). University Science Books, 2013. ISBN: 978-1-891389-85-6.
- Gérard Petit and Brian Luzum (Eds.). IERS Conventions (2010), IERS Technical Note No. 36, Frankfurt am Main: Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, 2010. ISBN: 3-89888-989-6.
- Deakin, R.E., 1998, 'Derivatives of the earth’s potentials'. Geomatics Research Australasia, No.68, June, 1998, pp. 31-60.
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CIO | Celestial Intermediate Origin |
| CIP | Celestial Intermediate Pole |
| CIRS | Celestial Intermediate Reference System |
| CEO | Celestial Ephemeris Origin |
| EGM | Earth Gravitational Model |
| GCRS | Geocentric Celestial Reference System |
| IAU | International Astronomical Union |
| IERS | International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service |
| ITRF | International Terrestrial Reference Frame |
| ITRS | International Terrestrial Reference System |
| TAI | International Atomic Time |
| TIO | Terrestrial Intermediate Origin |
| TIRS | Terrestrial Intermediate Reference System |
| TT | Terrestrial Time |
| UT1 | Universal Time |
| UTC | Coordinated Universal Time |
| WGS | World Geodetic System |