Virtualisation is the process of creating a virtual version of something. In this case, software simulates the functionality of hardware in a virtual environment.
- Increased IT productivity and agility
- Faster provisioning of applications and resources
- Reduced costs
Vagrant is a tool used to build and manage virtual machines in one workflow, with a specific focus on automation.
Virtual Box is a tool used to create virtual machines, in which, any operating system can be ran.
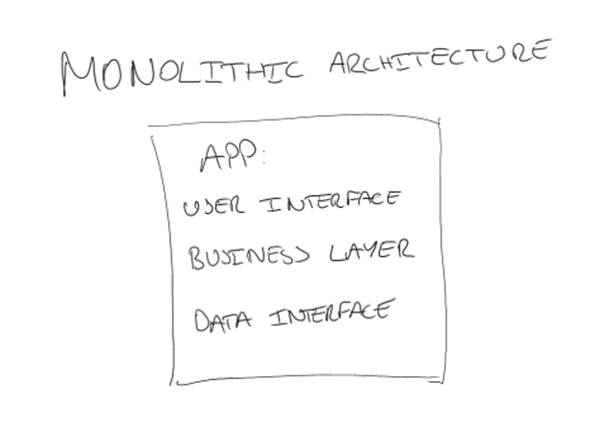
It is the traditional, unified model for the design of a software program, in which, all the code for a software product, is composed in one area. It is self-contained, so the components of the program are tightly coupled, rather than loosely coupled. Moreover, each component has to be present for the software to execute successfully. Programs, that are built using a monolithic architecture, tend to be a single large application.
- Easier to test and debug
- Easier to use this architecture; particularly at the start of the software development lifecycle
- Simpler usage due to to the singular codebase
- Better architecture for simple, lightweight applications
- Drawbacks become more prevalent as the complexity of the product increases
- The codebase can be difficult to understand, therefore making it difficult for developers to modify code
- For each update, developers must compile the entire codebase and then redeploy the full application, which is a very slow and costly process
- A bug in one component can potentially bring down the entire application
This is the capability of Vagrant to create multiple virtual machines within its Vagrantfile. The machines are associated with each other within a single environment.
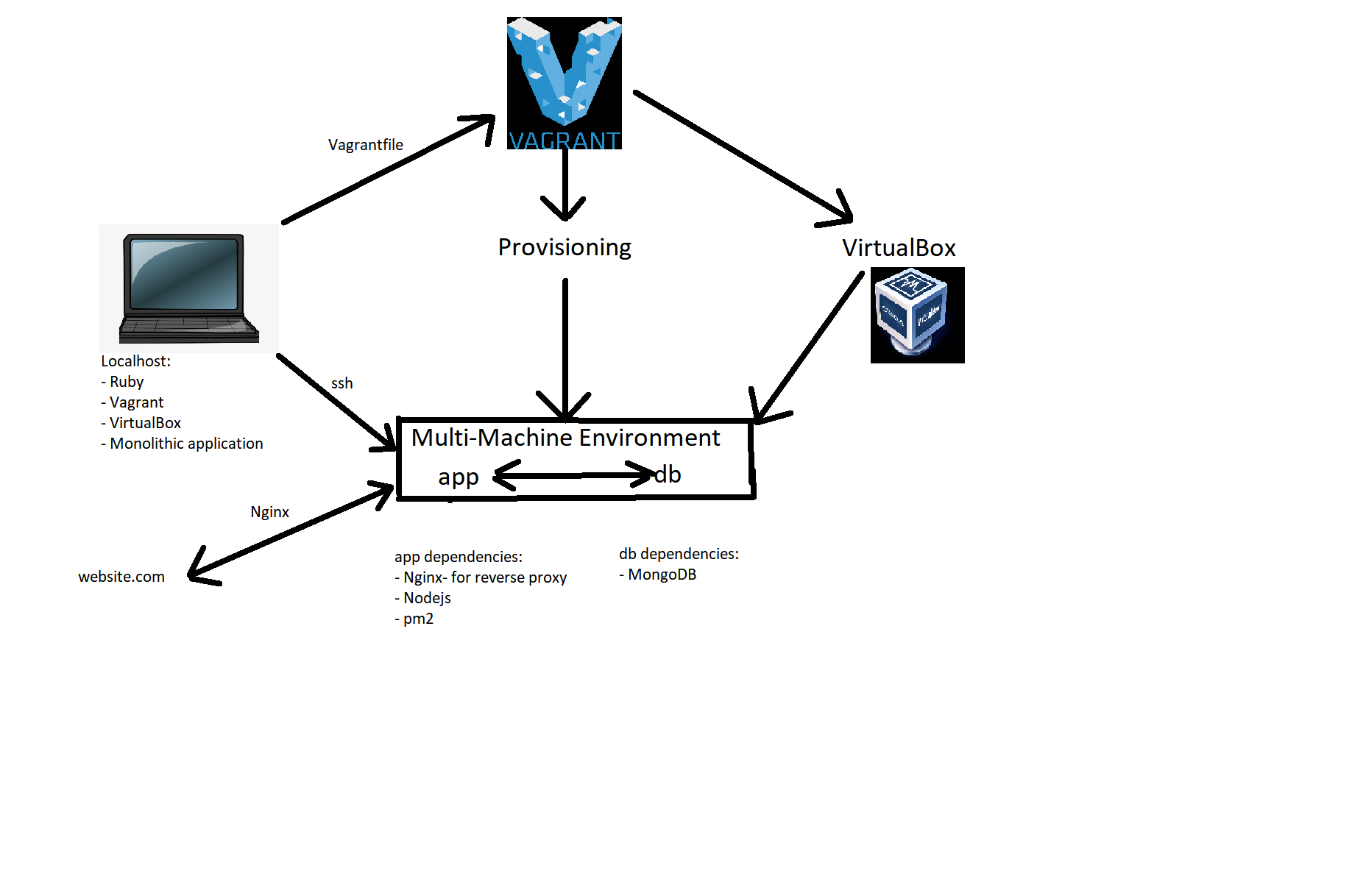
Diagram explained:
- Localhost with dependencies installed: Ruby, Vagrant, VirtualBox
- Vagrantfile with instructions to create two virtual machines in a single environment
- Vagrantfile includes the automation of the provisioning of the two virtual machines
- app VM needs to have Nginx, NodeJs and pm2 installed- to pass the tests
- app VM also needs to have an environment variable to enable a connection with the db vm
- db VM needs mongodb installed with all the relevant mongodb dependencies
- as these have all been provisioned the app should run when running the command in the app vm