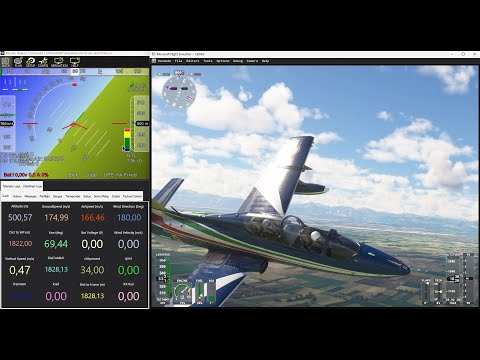
MSFS–ArduPilot Bridge is a lightweight Windows utility that connects Microsoft Flight Simulator (MSFS) with ArduPilot-based setups (SITL, companion tools, or integration utilities).
It uses SimConnect to read simulator state and exposes it via a JSON-over-UDP interface, specifically designed to feed the ArduPilot JSON backend.
The goal is to provide a simple bridge layer between a full-featured desktop simulator and the ArduPilot ecosystem, allowing you to fly ArduPilot SITL vehicles within the MSFS visual environment.
-
Bidirectional Bridge Connects MSFS (SimConnect) to ArduPilot SITL (JSON frame).
-
Multiple Positioning Modes
- MP SITL (Auto-Origin) – Automatically sets the local origin to the aircraft's starting position (ideal for Mission Planner's internal SITL to avoid coordinate jumps).
- Position – Uses a fixed origin defined in the configuration (sends local vector only).
- LLA – Uses a fixed origin but sends full Latitude/Longitude/Altitude + local vector (ideal for WSL2/global SITL setups when supported).
-
Joystick Integration Reads DirectInput devices and forwards axes/buttons to ArduPilot as RC overrides (no need for MAVLink joystick forwarding).
-
Compact C++ Codebase Minimal dependencies, focused on performance and clarity.
-
Persistent Configuration All interface settings are saved to a configuration file and loaded automatically upon startup.
-
SITL Sensor Debug All sensors coming from MSFS via SimConnect can be monitored in a live view popup window.
-
Sensor Logging If enabled, the software creates a CSV file containing all sensor data from SimConnect and other useful metrics for debugging or flight analysis.
- Microsoft Flight Simulator 2020 or 2024
- SimConnect SDK and
SimConnect.dll - Windows 10 or later
- Visual Studio 2022 (Desktop development with C++ workload)
- An ArduPilot SITL environment (Mission Planner internal SITL, WSL2, or standalone)
To run the bridge,
SimConnect.dllmust be present in the same folder asmsfs_ap_bridge.exe.
This DLL is not included in the distribution for copyright reasons.
To install the MSFS 2020/2024 SDK:
- Enable Developer Mode in MSFS.
- Use the new menu bar entry to download the SDK.
- Extract the downloaded ZIP and run the main installer.
- SimConnect and related headers/libraries will be installed on your system.
Prebuilt Windows binaries are available in the Releases section of this repository.
Download the latest .zip, extract it, and make sure that
SimConnect.dll is in the same folder as msfs_ap_bridge.exe
(see the SimConnect note above for details).
-
Get the sources
You can either clone the repository or download the ZIP archive.Clone with Git
git clone https://github.com/robustini/MSFSAPBridge.git
-
Open in Visual Studio
- Start Visual Studio 2022.
File → Open → Folder....- Select the folder containing
CMakeLists.txt.
Visual Studio will automatically configure the CMake project via CMake.
-
Build
- Select configuration:
Release/x64. - Build the project (e.g. Build → Build All).
The executable
msfs_ap_bridge.exewill be generated in the build output directory for the selected configuration. - Select configuration:
- Launch MSFS and spawn your aircraft at the desired location (airport, runway, etc.).
- Optionally choose a joystick as your primary control device.
- Important: remove or unbind control-surface and throttle assignments for that joystick inside MSFS.
These controls will instead be driven by ArduPilot via the bridge, avoiding overlapping or conflicting inputs.
- Run
msfs_ap_bridge.exe. - In the SITL Connection and Status section, leave the initial defaults:
- IP:
127.0.0.1(localhost) - Ports: TX =
9003, RX =9002 - Position mode:
MP SITL(recommended for Mission Planner’s internal SITL)
- IP:
- Select the joystick you want to use as ArduPilot's RC input from the joystick dropdown.
The status LEDs will indicate connectivity for Sim, TX, RX, and joystick.
The bridge expects JSON frame SITL output. Because the stock ArduPilot SITL bundled with Mission Planner cannot ingest external simulator coordinates directly, you must replace its executable with a custom JSON-enabled build.
- Download the custom
ArduPlane.exe(Google Drive link). - Close Mission Planner.
- Navigate to:
Documents\Mission Planner\sitl - Copy the downloaded
ArduPlane.exeinto this folder, overwriting the existing file.
Mission Planner will continue to work normally, but its internal SITL will now use the JSON-capable backend required by the bridge.
- Open Mission Planner.
- Go to the Simulation tab.
- In the Options dropdown, select Skip Download (so Mission Planner does not restore the original ArduPlane.exe).
- In Model, choose
plane(or the vehicle type you want to simulate). - In Extra command line, enter:
--model json - Click the plane icon at the bottom to start SITL.
Once SITL is running, the bridge should show green indicators for all SITL-related signals.
For this workflow, set the bridge Position mode = LLA.
Note
Due to limits in ArduPilot’s current SITL implementation, the simulator cannot directly accept full Lat/Lon/Alt from an external source.
The custom ArduPlane executable partially alleviates this, but the bridge must still operate in LLA mode when using Mission Planner’s internal SITL.
You can also run ArduPilot SITL from WSL2 or a native Linux environment using sim_vehicle.py with the JSON backend enabled.
Example:
sim_vehicle.py -v ArduPlane -f json --sim-address 172.26.16.1 --console --mapWhere 172.26.16.1 is the Windows host IP as seen from WSL2.
Enter the same IP in the bridge configuration so the bridge can send sensor data to SITL.
By default, ArduPilot's JSON backend cannot properly accept full geographic coordinates (Lat/Lon/Alt) from an external simulator.
Because of this limitation, the classic Position mode of the bridge is not recommended: it works, but results in unreliable world-frame alignment and poor long-range accuracy.
To enable proper external-sim LLA input, you must compile ArduPilot with the following pull request applied:
When running a firmware built with that PR, you should always use Position mode = LLA in the bridge.
In this configuration, MSFS sends full Lat/Lon/Alt + local vector to SITL, enabling correct georeferencing and stable alignment throughout the flight.
On first launch, the application automatically creates a configuration file
with the same name as the executable (by default msfs_ap_bridge.ini)
in the same folder.
Manual creation or editing of this file is usually unnecessary: settings can be
changed from the UI and are saved back to the .ini file.
The example below is only for reference or advanced/manual tweaking.
[bridge]
# Target IP for ArduPilot SITL (usually localhost)
ip = 127.0.0.1
# Ports must match your SITL configuration
port_tx = 9003 ; Bridge sends sensor data to SITL on this port
port_rx = 9002 ; Bridge receives PWM/servo data from SITL on this port
# Simulation rate (Hz)
rate = 1000
# Positioning Mode (crucial for stability)
# 0 = MP SITL (Auto-origin for Mission Planner SITL)
# 1 = Position (fixed origin, sends local vector)
# 2 = LLA (fixed origin, sends Lat/Lon/Alt + vector)
pos_mode = 0Other options (not shown here) allow control of resampling, timing, and other advanced behaviors.
The most delicate part of the setup is making ArduPilot "accept" your joystick mapping through the bridge.
- Map joystick axes and buttons to the desired RC channels.
- Use the reverse options in the bridge UI (not in ArduPilot) to correct directions as needed.
- Treat the bridge as your “virtual RC radio” for SITL.
- Leave RC mapping and modes mostly at their defaults where possible.
- Perform a standard Radio Calibration (especially if using an actual RC transmitter forwarded into the system).
- Configure ArduPlane (or your chosen vehicle type) according to the official ArduPilot documentation.
The following parameters are particularly important for stable operation with MSFS via the bridge:
AHRS_EKF_TYPE = 10GPS1_TYPE = 100INS_GYR_CAL = 0
Refer to the ArduPilot wiki for full context and tuning details.
This project is licensed under the GNU General Public License v3.0 (GPLv3).
You are free to use, study, modify, and redistribute this software under the terms of the GPLv3.
See the LICENSE file in the repository root for the full license text.
Contributions are welcome!
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Commit your changes with clear messages
- Open a pull request describing the motivation and behavior of your changes
Bug reports and feature suggestions are also appreciated.
MSFS–ArduPilot Bridge is developed by Marco Robustini (aka Marcopter).
It is intended as a clean, focused utility that bridges the visual fidelity of MSFS with the advanced autopilot capabilities of ArduPilot SITL.
Follow the author: